- Public Group
- 123 Posts
- 97 Photos
- 15 Videos
- Cars and Vehicles
Recent Updates
- Please log in to like, share and comment!
- https://youtu.be/dCIN352Ly3I?si=wdY12HH_cYaNkwkd
 0 Comments 0 Shares 38 Views
0 Comments 0 Shares 38 Views - https://youtu.be/cbrvHPc3Vug?si=NdZRLi0wIZDyyMSS
 0 Comments 0 Shares 37 Views
0 Comments 0 Shares 37 Views - https://youtu.be/fYj6GIaFTHk?si=lINbenqaKGUp5W6l
 0 Comments 0 Shares 37 Views
0 Comments 0 Shares 37 Views - Su-57 Felon (Russia) vs F-35 Lightening II (USA) | Aircraft Specifications Comparison #usa #russia0 Comments 0 Shares 48 Views
-
-
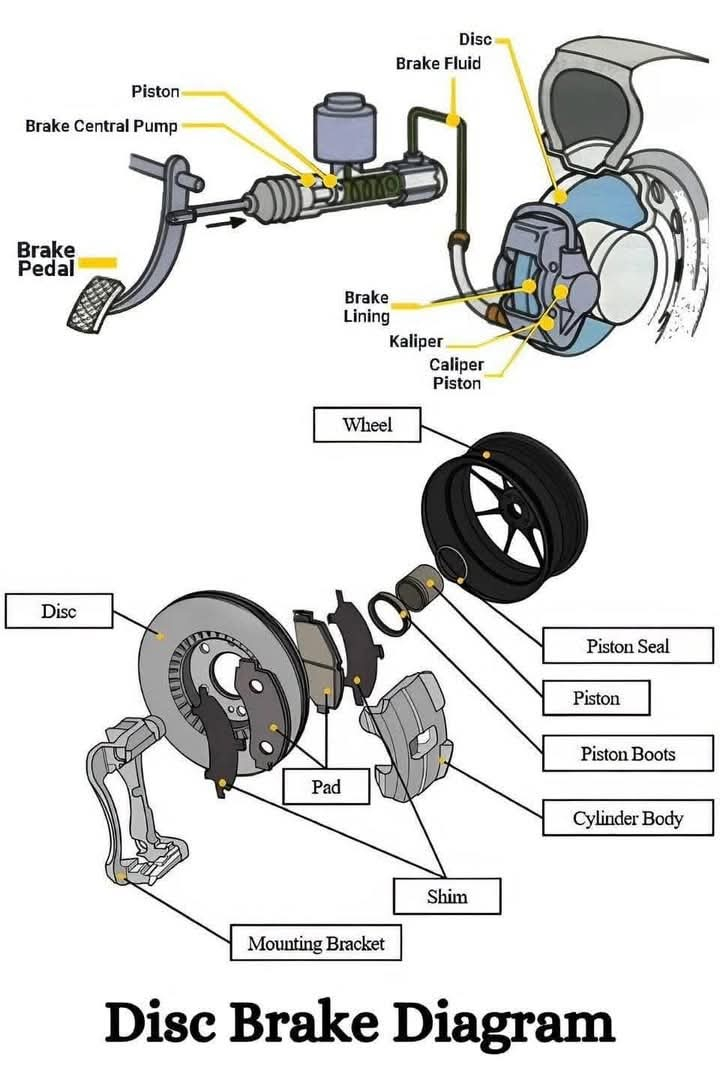
- Parts of a Disc Brake:
1. Brake Disc (Rotor): A rotating metal disc attached to the wheel.
2. Brake Caliper: Houses pistons and brake pads; it applies pressure to the disc.
3. Brake Pads: Friction material that presses against the disc.
4. Brake Fluid: Transfers force from the brake pedal to the caliper.
5. Pistons: Hydraulic components in the caliper that push the brake pads.
Working of a Disc Brake:
When the brake pedal is pressed, brake fluid from the master cylinder exerts hydraulic pressure on the pistons in the caliper. This pushes the brake pads against the rotating disc, creating friction that slows down the wheel. Once the pedal is released, the brake pads retract, and the disc rotates freely.
Advantages:
1. Effective Heat Dissipation: Reduces the risk of brake fade.
2. Superior Stopping Power: Offers consistent braking performance.
3. Low Maintenance: Easier to inspect and replace compared to drum brakes.
4. Improved Durability: Less prone to warping under heavy use.
Symptoms of Faulty Disc Brakes:
1. Squealing Noise: Indicates worn-out brake pads.
2. Vibrations: Suggests a warped disc or uneven wear.
3. Reduced Braking Efficiency: May indicate air in the brake lines or fluid issues.
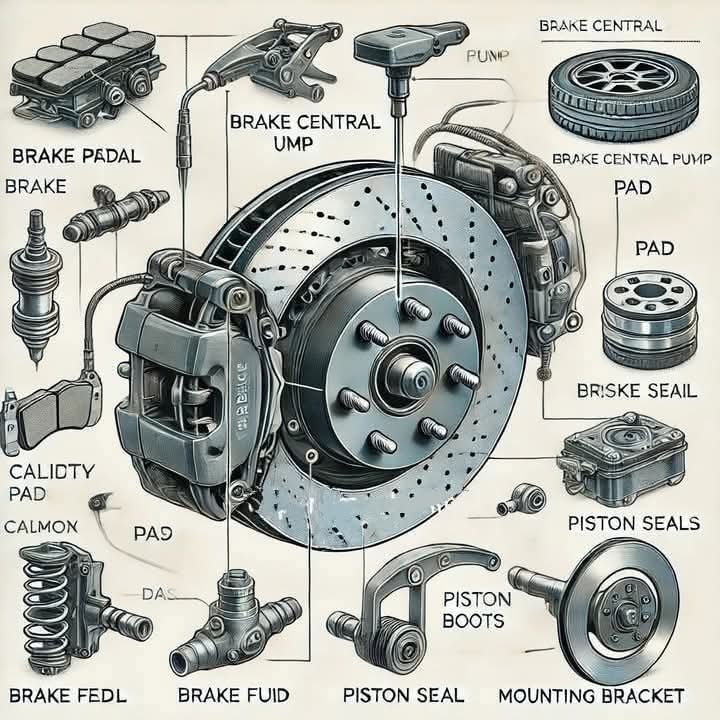
4. Pulling to One Side: Caused by uneven caliper function or pad wear.Parts of a Disc Brake: 1. Brake Disc (Rotor): A rotating metal disc attached to the wheel. 2. Brake Caliper: Houses pistons and brake pads; it applies pressure to the disc. 3. Brake Pads: Friction material that presses against the disc. 4. Brake Fluid: Transfers force from the brake pedal to the caliper. 5. Pistons: Hydraulic components in the caliper that push the brake pads. Working of a Disc Brake: When the brake pedal is pressed, brake fluid from the master cylinder exerts hydraulic pressure on the pistons in the caliper. This pushes the brake pads against the rotating disc, creating friction that slows down the wheel. Once the pedal is released, the brake pads retract, and the disc rotates freely. Advantages: 1. Effective Heat Dissipation: Reduces the risk of brake fade. 2. Superior Stopping Power: Offers consistent braking performance. 3. Low Maintenance: Easier to inspect and replace compared to drum brakes. 4. Improved Durability: Less prone to warping under heavy use. Symptoms of Faulty Disc Brakes: 1. Squealing Noise: Indicates worn-out brake pads. 2. Vibrations: Suggests a warped disc or uneven wear. 3. Reduced Braking Efficiency: May indicate air in the brake lines or fluid issues. 4. Pulling to One Side: Caused by uneven caliper function or pad wear.0 Comments 0 Shares 129 Views - a brake system, likely for a car. Here's a breakdown of the labeled components:
Main Components:
* Brake Pedal: The driver applies pressure to this pedal to initiate braking.
* Brake Central Pump: This is the heart of the hydraulic braking system. It converts the mechanical pressure from the pedal into hydraulic pressure.
* Brake Pad: These friction pads are mounted on the caliper and press against the brake rotor to slow down the vehicle.
* Brake Rotor: A metal disc that rotates with the wheel. The brake pads clamp onto it to create friction and slow down the wheel.
* Caliper: A housing that holds the brake pads and applies pressure to them against the rotor.
* Piston: Located within the caliper, these push the brake pads against the rotor when hydraulic pressure is applied.
* Piston Seals: These prevent brake fluid from leaking past the piston.
* Piston Boots: These protect the piston seals from dirt and debris.
* Brake Fluid: This incompressible fluid transmits pressure from the master cylinder to the calipers.
* Brake Field: This likely refers to the area where the brake system operates, such as the wheels or the brake lines.
* Mounting Bracket: This attaches the caliper to the vehicle's suspension.
Other Components:
* Brisk Seal: This is likely a type of seal used in the brake system.
* Calidity Calmon: This might refer to a type of brake pad material or a brand.
Overall, the image provides a comprehensive view of the key components involved in a typical hydraulic brake system and how they work together to slow down and stop a vehicle.
#automotive #mechaniclife #cars #mechanical #mechanic #carparts #restoration #viral #carmemes #usa
#fypシ #autos #automobile #mechanic #mechanical #engineering #cars #engine #sensors #usaa brake system, likely for a car. Here's a breakdown of the labeled components: Main Components: * Brake Pedal: The driver applies pressure to this pedal to initiate braking. * Brake Central Pump: This is the heart of the hydraulic braking system. It converts the mechanical pressure from the pedal into hydraulic pressure. * Brake Pad: These friction pads are mounted on the caliper and press against the brake rotor to slow down the vehicle. * Brake Rotor: A metal disc that rotates with the wheel. The brake pads clamp onto it to create friction and slow down the wheel. * Caliper: A housing that holds the brake pads and applies pressure to them against the rotor. * Piston: Located within the caliper, these push the brake pads against the rotor when hydraulic pressure is applied. * Piston Seals: These prevent brake fluid from leaking past the piston. * Piston Boots: These protect the piston seals from dirt and debris. * Brake Fluid: This incompressible fluid transmits pressure from the master cylinder to the calipers. * Brake Field: This likely refers to the area where the brake system operates, such as the wheels or the brake lines. * Mounting Bracket: This attaches the caliper to the vehicle's suspension. Other Components: * Brisk Seal: This is likely a type of seal used in the brake system. * Calidity Calmon: This might refer to a type of brake pad material or a brand. Overall, the image provides a comprehensive view of the key components involved in a typical hydraulic brake system and how they work together to slow down and stop a vehicle. #automotive #mechaniclife #cars #mechanical #mechanic #carparts #restoration #viral #carmemes #usa #fypシ #autos #automobile #mechanic #mechanical #engineering #cars #engine #sensors #usa0 Comments 0 Shares 121 Views - Evolution Of Rolls RoyceEvolution Of Rolls Royce0 Comments 0 Shares 115 Views
More Stories