- Grupo público
- 84 Publicações
- 74 fotos
- 5 Vídeos
- Cars and Vehicles
- 0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 11 VisualizaçõesFaça o login para curtir, compartilhar e comentar!
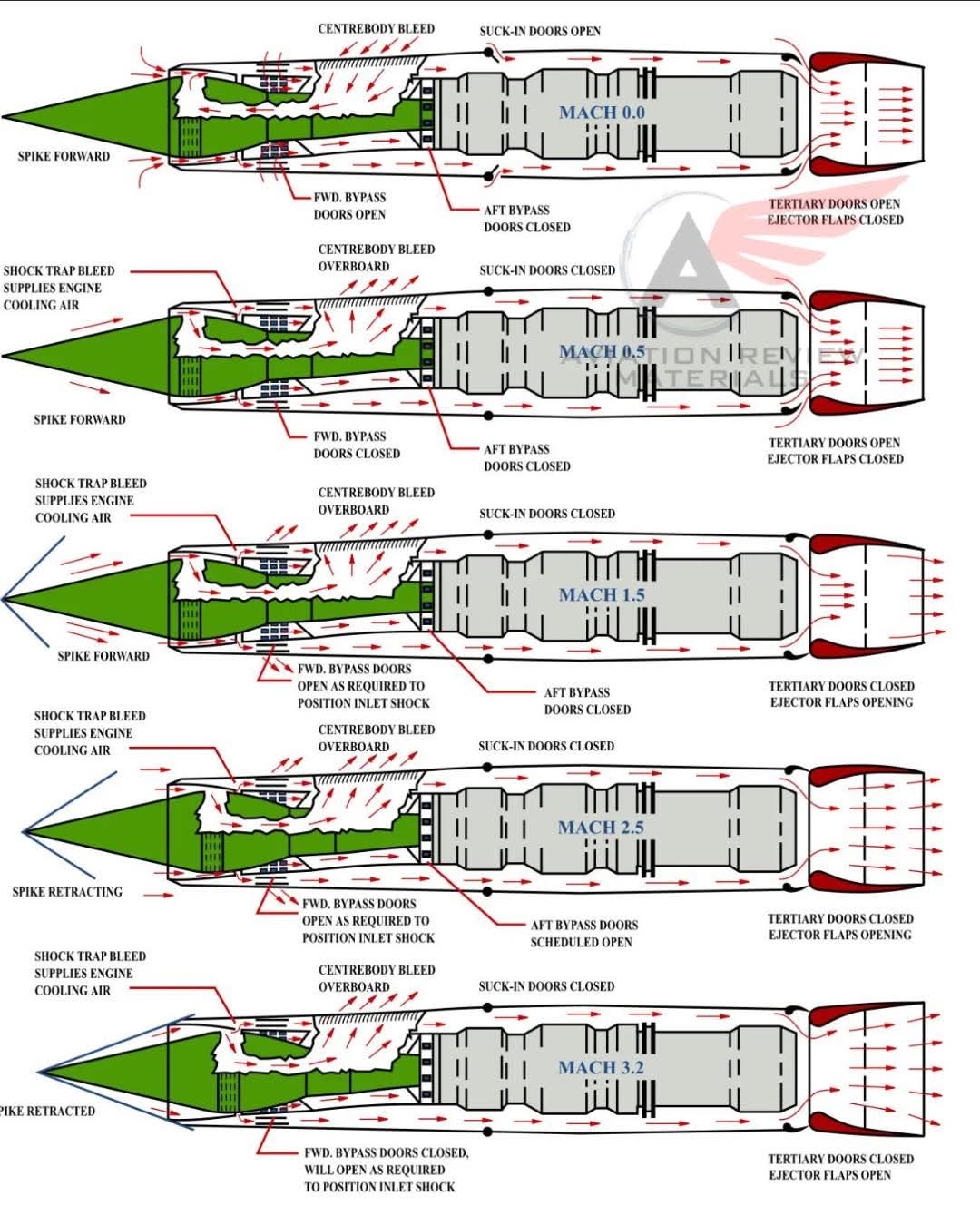
- Ever wondered how a jet engine on a supersonic aircraft can breathe at both takeoff and at three times the speed of sound? This diagram reveals the complex dance of moving parts inside a variable geometry inlet—like those used on the legendary SR-71 Blackbird—to keep airflow to the engine just right at every speed.
At low speeds (Mach 0–0.5), suck-in doors and tertiary doors open wide to feed the engine plenty of air. As speed increases, the system gradually closes these openings, using forward bypass doors and centrebody bleeds to manage airflow and prevent compressor stalls. Past Mach 1.5, the inlet spike starts retracting, creating controlled shockwaves to slow the air before it enters the engine—because jet turbines can’t handle supersonic airflow directly.
By Mach 3.2, every door and bleed is precisely positioned, the spike is fully retracted, and the engine runs in a delicate balance of pressure, temperature, and airflow. This engineering ballet lets a high-speed aircraft cruise faster than a rifle bullet without melting its engines.
At Mach 3, every millisecond and millimeter matters.
#SupersonicEngineering #JetEngines #SR71 #AviationTech #Mach3Ever wondered how a jet engine on a supersonic aircraft can breathe at both takeoff and at three times the speed of sound? This diagram reveals the complex dance of moving parts inside a variable geometry inlet—like those used on the legendary SR-71 Blackbird—to keep airflow to the engine just right at every speed. At low speeds (Mach 0–0.5), suck-in doors and tertiary doors open wide to feed the engine plenty of air. As speed increases, the system gradually closes these openings, using forward bypass doors and centrebody bleeds to manage airflow and prevent compressor stalls. Past Mach 1.5, the inlet spike starts retracting, creating controlled shockwaves to slow the air before it enters the engine—because jet turbines can’t handle supersonic airflow directly. By Mach 3.2, every door and bleed is precisely positioned, the spike is fully retracted, and the engine runs in a delicate balance of pressure, temperature, and airflow. This engineering ballet lets a high-speed aircraft cruise faster than a rifle bullet without melting its engines. 🔥 At Mach 3, every millisecond and millimeter matters. #SupersonicEngineering #JetEngines #SR71 #AviationTech #Mach30 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 46 Visualizações - In 1991, Mazda made motorsport history by becoming the first — and still the only — Japanese car maker to win the 24 Hours of Le Mans.
The victory came with the legendary Mazda 787B prototype, a machine powered by one of the most unique and iconic engines ever to race: the R26B quad-rotor Wankel rotary engine. Producing around 700 horsepower, this naturally aspirated engine was a high-revving beast, famous for its iconic exhaust note and incredible power-to-weight ratio.
The R26B used four rotors and featured exotic technologies like three spark plugs per rotor and continuously variable intake runners. With a redline well over 9,000 rpm, it delivered linear power and exceptional reliability over the grueling 24-hour race. Unlike conventional piston engines, the rotary engine had far fewer moving parts, which helped reduce weight and improve durability at high RPMs.
Mazda’s victory wasn’t just about speed—it was a triumph of innovation and perseverance. The 787B’s lightweight construction, efficient aerodynamics, and dependable rotary engine all contributed to the historic win. After the 1991 race, rotary engines were banned from Le Mans competition, which has only added more weight to the legendary status of the 787B and its wailing, fire-spitting heart. #MazdaIn 1991, Mazda made motorsport history by becoming the first — and still the only — Japanese car maker to win the 24 Hours of Le Mans. The victory came with the legendary Mazda 787B prototype, a machine powered by one of the most unique and iconic engines ever to race: the R26B quad-rotor Wankel rotary engine. Producing around 700 horsepower, this naturally aspirated engine was a high-revving beast, famous for its iconic exhaust note and incredible power-to-weight ratio. The R26B used four rotors and featured exotic technologies like three spark plugs per rotor and continuously variable intake runners. With a redline well over 9,000 rpm, it delivered linear power and exceptional reliability over the grueling 24-hour race. Unlike conventional piston engines, the rotary engine had far fewer moving parts, which helped reduce weight and improve durability at high RPMs. Mazda’s victory wasn’t just about speed—it was a triumph of innovation and perseverance. The 787B’s lightweight construction, efficient aerodynamics, and dependable rotary engine all contributed to the historic win. After the 1991 race, rotary engines were banned from Le Mans competition, which has only added more weight to the legendary status of the 787B and its wailing, fire-spitting heart. #Mazda0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 48 Visualizações - https://www.facebook.com/share/p/19aaSR2AU4/WWW.FACEBOOK.COMICTV PH - In 1991, Mazda made motorsport history by...In 1991, Mazda made motorsport history by becoming the first — and still the only — Japanese car maker to win the 24 Hours of Le Mans. The victory came with the legendary Mazda 787B prototype, a...0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 49 Visualizações
- 0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 59 Visualizações
- 0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 68 Visualizações
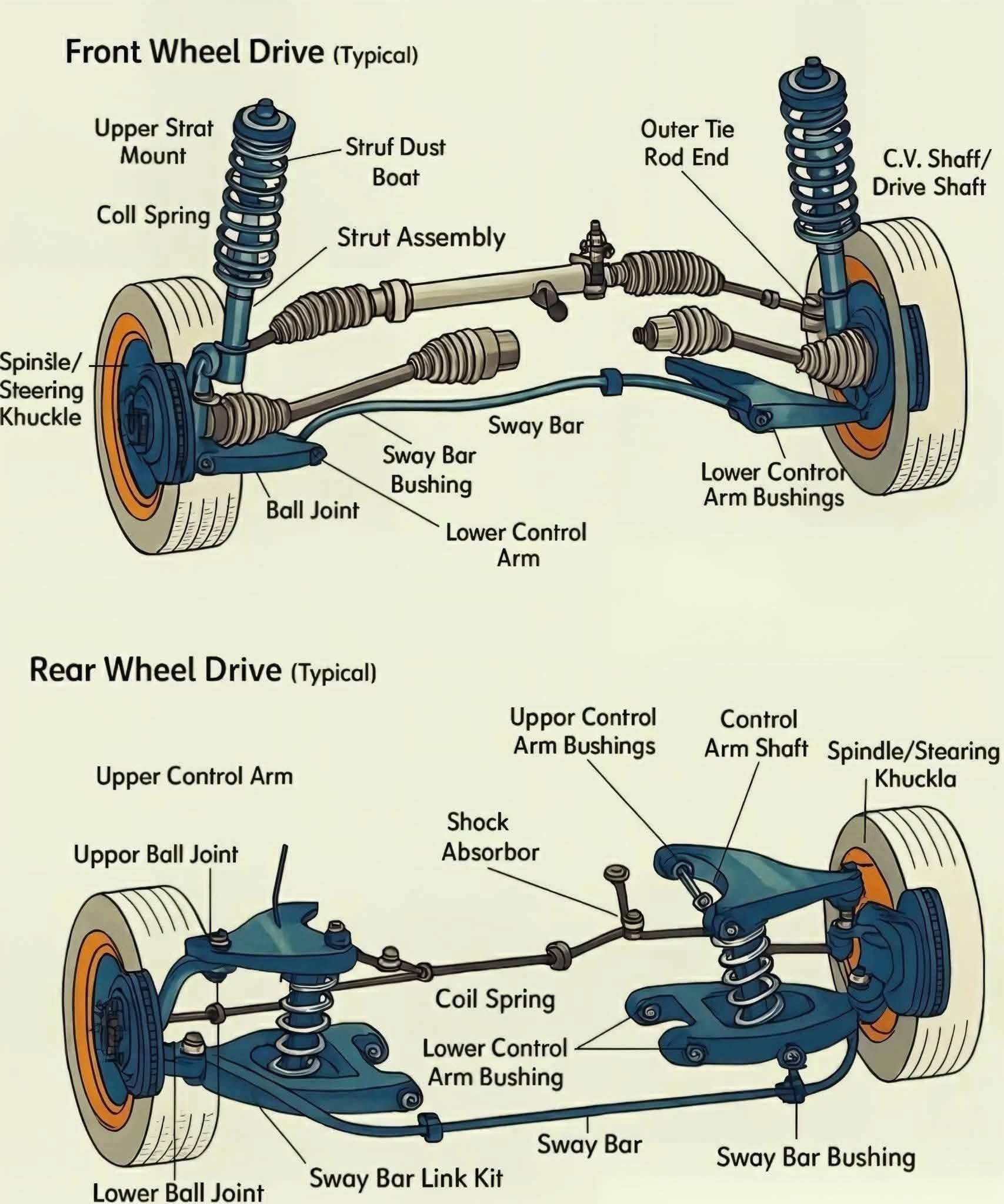
- A comparison between the suspension systems used in front-wheel drive (FWD) and rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles, highlighting major components:
Front-Wheel Drive Suspension
Control Arm: Connects the wheel hub to the vehicle frame; allows vertical movement.
Stabilizer Bar (Anti-roll bar): Reduces body roll during cornering.
Helicoidal Spring: Absorbs shocks from the road.
Dampening Set (Shock Absorber): Controls spring movement, reducing bounce.
Note: In FWD cars, the suspension must also accommodate steering and power delivery to the front wheels, making it more compact and complex.
Rear-Wheel Drive Suspension
Control Arm: Provides wheel alignment and support.
Stabilizer Bar: Prevents excessive body roll.
Helicoidal Spring: Supports vehicle weight and absorbs shocks.
Dampening Set: Same function as in FWD.
Driveshaft: Transfers power from the engine (at the front) to the rear wheels.
Note: RWD setups generally allow for better weight distribution and are simpler at the front since the wheels only steer, not drive.
Key Difference
FWD: More compact, front handles both steering and power.
RWD: Power sent to the rear, front handles only steering — often gives better balance and handling in performance vehicles.
#mechanic #automotive #machinelearning #mechaniclife #automobileA comparison between the suspension systems used in front-wheel drive (FWD) and rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles, highlighting major components: 🔧 Front-Wheel Drive Suspension Control Arm: Connects the wheel hub to the vehicle frame; allows vertical movement. Stabilizer Bar (Anti-roll bar): Reduces body roll during cornering. Helicoidal Spring: Absorbs shocks from the road. Dampening Set (Shock Absorber): Controls spring movement, reducing bounce. Note: In FWD cars, the suspension must also accommodate steering and power delivery to the front wheels, making it more compact and complex. 🔧 Rear-Wheel Drive Suspension Control Arm: Provides wheel alignment and support. Stabilizer Bar: Prevents excessive body roll. Helicoidal Spring: Supports vehicle weight and absorbs shocks. Dampening Set: Same function as in FWD. Driveshaft: Transfers power from the engine (at the front) to the rear wheels. Note: RWD setups generally allow for better weight distribution and are simpler at the front since the wheels only steer, not drive. 🚗 Key Difference FWD: More compact, front handles both steering and power. RWD: Power sent to the rear, front handles only steering — often gives better balance and handling in performance vehicles. #mechanic #automotive #machinelearning #mechaniclife #automobile0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 70 Visualizações - 1972 Oldsmobile Cutlass Supreme1972 Oldsmobile Cutlass Supreme0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 78 Visualizações
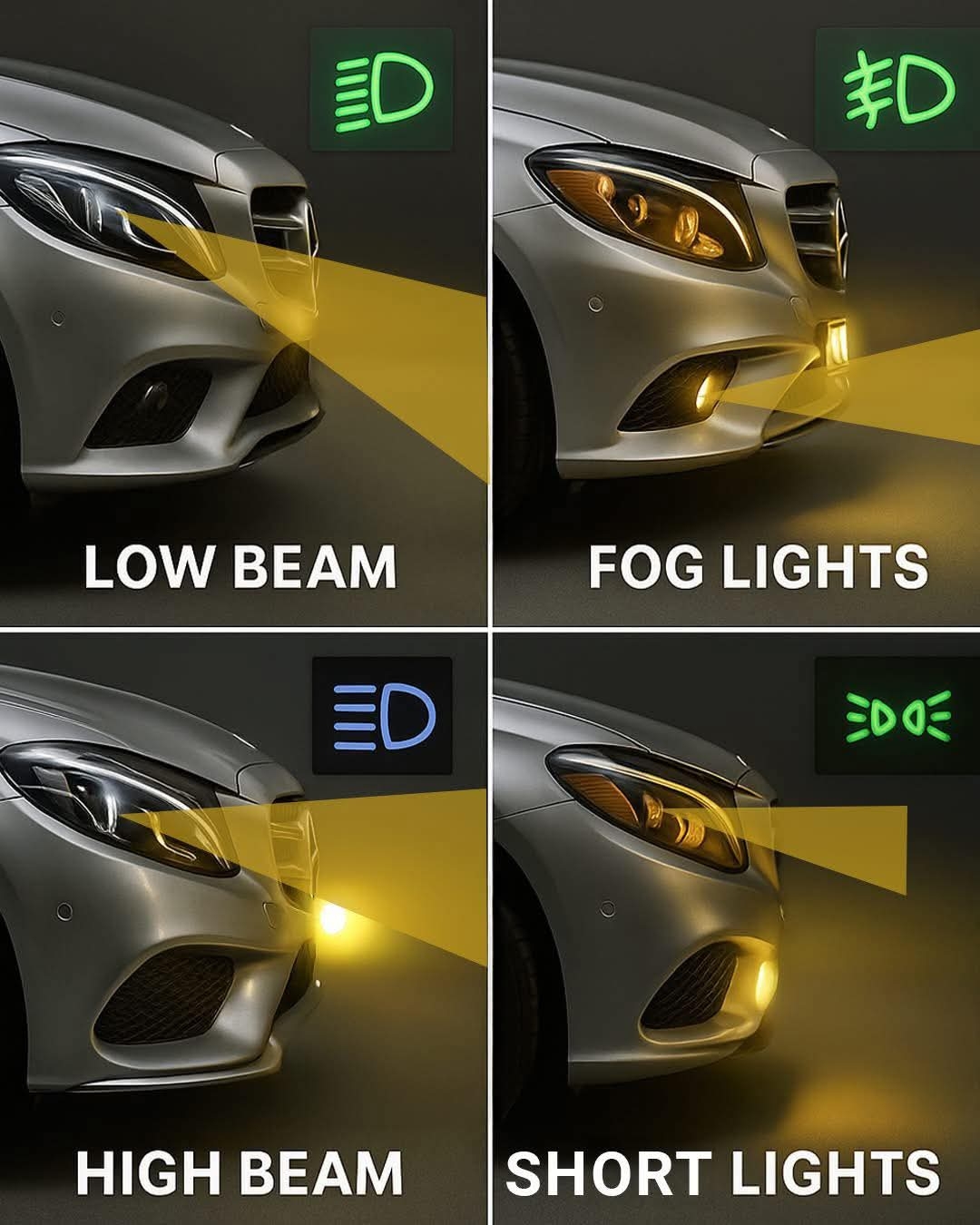
- Your headlights decodedYour headlights decoded0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 75 Visualizações
- 0 Comentários 0 Compartilhamentos 78 Visualizações
Mais stories