Brake Types Explained: Drum, Disc, Air & More – Which One Keeps You Safest?
Brakes are critical for vehicle safety, and different types serve specific purposes depending on the vehicle and application. Here are the main types of brakes:
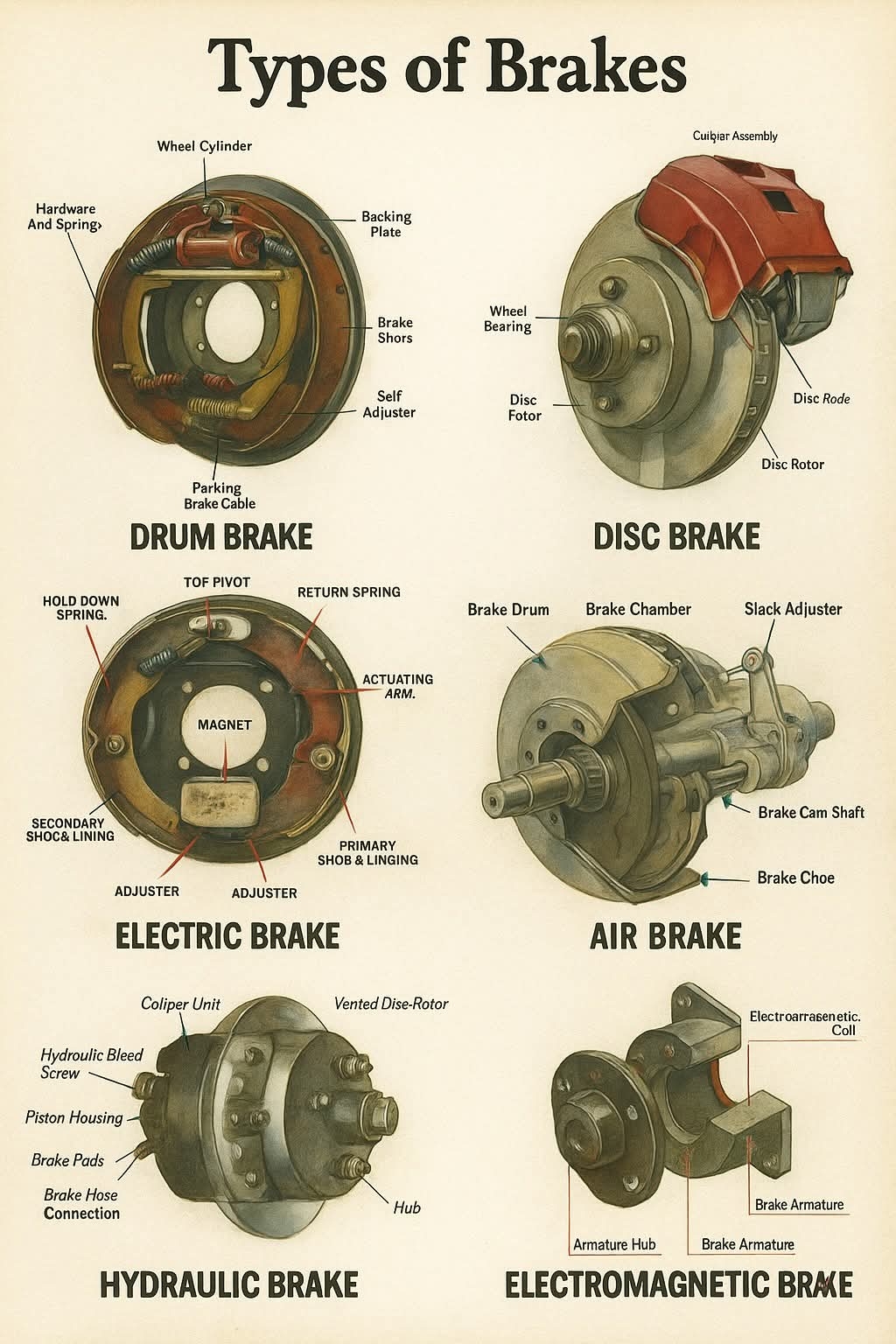
1. Drum Brake:
This traditional braking system consists of a drum attached to the wheel. When the brake pedal is pressed, brake shoes inside the drum expand outward and press against the drum, creating friction to stop the wheel. Drum brakes are simple and cost-effective, often used in rear wheels of cars.
2. Disc Brake:
Commonly used in modern cars, disc brakes use a rotating disc (rotor) and a stationary caliper. The caliper squeezes brake pads against the disc to create friction and slow the vehicle. Disc brakes provide better cooling and stopping power, especially in high-speed conditions.
3. Electric Brake:
Electric brakes are mostly used in trailers and some electric vehicles. They use an electric actuator to apply force to the brake shoes or pads. These are controlled by the vehicle's electrical system and are quieter with minimal maintenance.
4. Air Brake:
Used in heavy-duty vehicles like trucks and buses, air brakes rely on compressed air to push brake pads against the drum or disc. They offer powerful braking and fail-safe operation since the system automatically activates if air pressure drops.
6. Hydraulic Brake:
This is the most common system in passenger cars. When the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic fluid transfers force from the master cylinder to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders, causing braking action. It's reliable and provides consistent braking force.
7. Electromagnetic Brake:
Commonly found in trains and electric vehicles, these brakes use magnetic force to create resistance. They have no physical contact between moving parts, which means less wear and tear and quiet operation.
Brakes are critical for vehicle safety, and different types serve specific purposes depending on the vehicle and application. Here are the main types of brakes:
1. Drum Brake:
This traditional braking system consists of a drum attached to the wheel. When the brake pedal is pressed, brake shoes inside the drum expand outward and press against the drum, creating friction to stop the wheel. Drum brakes are simple and cost-effective, often used in rear wheels of cars.
2. Disc Brake:
Commonly used in modern cars, disc brakes use a rotating disc (rotor) and a stationary caliper. The caliper squeezes brake pads against the disc to create friction and slow the vehicle. Disc brakes provide better cooling and stopping power, especially in high-speed conditions.
3. Electric Brake:
Electric brakes are mostly used in trailers and some electric vehicles. They use an electric actuator to apply force to the brake shoes or pads. These are controlled by the vehicle's electrical system and are quieter with minimal maintenance.
4. Air Brake:
Used in heavy-duty vehicles like trucks and buses, air brakes rely on compressed air to push brake pads against the drum or disc. They offer powerful braking and fail-safe operation since the system automatically activates if air pressure drops.
6. Hydraulic Brake:
This is the most common system in passenger cars. When the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic fluid transfers force from the master cylinder to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders, causing braking action. It's reliable and provides consistent braking force.
7. Electromagnetic Brake:
Commonly found in trains and electric vehicles, these brakes use magnetic force to create resistance. They have no physical contact between moving parts, which means less wear and tear and quiet operation.
🚦 Brake Types Explained: Drum, Disc, Air & More – Which One Keeps You Safest?
Brakes are critical for vehicle safety, and different types serve specific purposes depending on the vehicle and application. Here are the main types of brakes:
1. Drum Brake:
This traditional braking system consists of a drum attached to the wheel. When the brake pedal is pressed, brake shoes inside the drum expand outward and press against the drum, creating friction to stop the wheel. Drum brakes are simple and cost-effective, often used in rear wheels of cars.
2. Disc Brake:
Commonly used in modern cars, disc brakes use a rotating disc (rotor) and a stationary caliper. The caliper squeezes brake pads against the disc to create friction and slow the vehicle. Disc brakes provide better cooling and stopping power, especially in high-speed conditions.
3. Electric Brake:
Electric brakes are mostly used in trailers and some electric vehicles. They use an electric actuator to apply force to the brake shoes or pads. These are controlled by the vehicle's electrical system and are quieter with minimal maintenance.
4. Air Brake:
Used in heavy-duty vehicles like trucks and buses, air brakes rely on compressed air to push brake pads against the drum or disc. They offer powerful braking and fail-safe operation since the system automatically activates if air pressure drops.
6. Hydraulic Brake:
This is the most common system in passenger cars. When the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic fluid transfers force from the master cylinder to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders, causing braking action. It's reliable and provides consistent braking force.
7. Electromagnetic Brake:
Commonly found in trains and electric vehicles, these brakes use magnetic force to create resistance. They have no physical contact between moving parts, which means less wear and tear and quiet operation.
0 Comments
0 Shares
131 Views