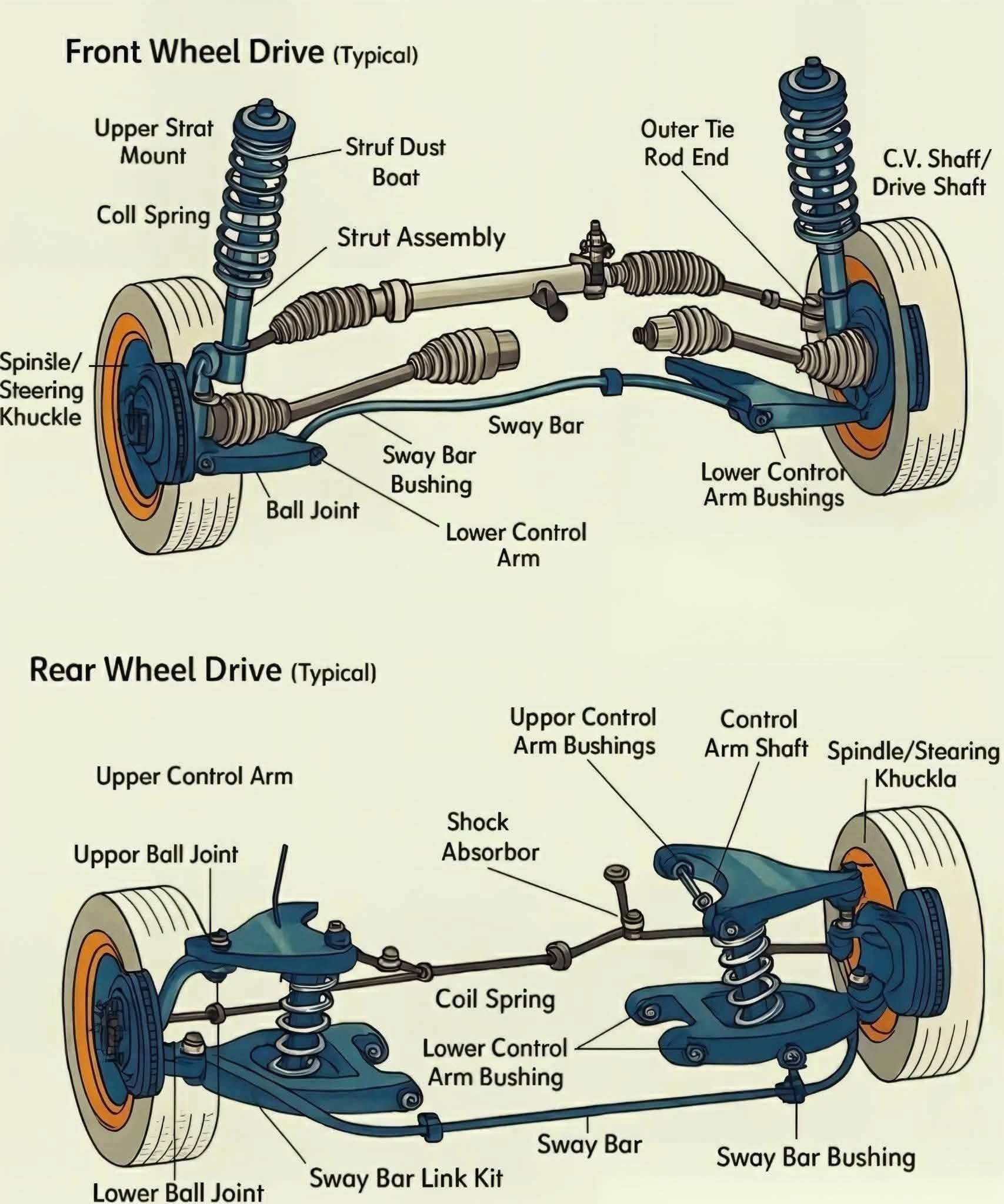
A comparison between the suspension systems used in front-wheel drive (FWD) and rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles, highlighting major components:
Front-Wheel Drive Suspension
Control Arm: Connects the wheel hub to the vehicle frame; allows vertical movement.
Stabilizer Bar (Anti-roll bar): Reduces body roll during cornering.
Helicoidal Spring: Absorbs shocks from the road.
Dampening Set (Shock Absorber): Controls spring movement, reducing bounce.
Note: In FWD cars, the suspension must also accommodate steering and power delivery to the front wheels, making it more compact and complex.
Rear-Wheel Drive Suspension
Control Arm: Provides wheel alignment and support.
Stabilizer Bar: Prevents excessive body roll.
Helicoidal Spring: Supports vehicle weight and absorbs shocks.
Dampening Set: Same function as in FWD.
Driveshaft: Transfers power from the engine (at the front) to the rear wheels.
Note: RWD setups generally allow for better weight distribution and are simpler at the front since the wheels only steer, not drive.
Key Difference
FWD: More compact, front handles both steering and power.
RWD: Power sent to the rear, front handles only steering — often gives better balance and handling in performance vehicles.
#mechanic #automotive #machinelearning #mechaniclife #automobile
Front-Wheel Drive Suspension
Control Arm: Connects the wheel hub to the vehicle frame; allows vertical movement.
Stabilizer Bar (Anti-roll bar): Reduces body roll during cornering.
Helicoidal Spring: Absorbs shocks from the road.
Dampening Set (Shock Absorber): Controls spring movement, reducing bounce.
Note: In FWD cars, the suspension must also accommodate steering and power delivery to the front wheels, making it more compact and complex.
Rear-Wheel Drive Suspension
Control Arm: Provides wheel alignment and support.
Stabilizer Bar: Prevents excessive body roll.
Helicoidal Spring: Supports vehicle weight and absorbs shocks.
Dampening Set: Same function as in FWD.
Driveshaft: Transfers power from the engine (at the front) to the rear wheels.
Note: RWD setups generally allow for better weight distribution and are simpler at the front since the wheels only steer, not drive.
Key Difference
FWD: More compact, front handles both steering and power.
RWD: Power sent to the rear, front handles only steering — often gives better balance and handling in performance vehicles.
#mechanic #automotive #machinelearning #mechaniclife #automobile
A comparison between the suspension systems used in front-wheel drive (FWD) and rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles, highlighting major components:
🔧 Front-Wheel Drive Suspension
Control Arm: Connects the wheel hub to the vehicle frame; allows vertical movement.
Stabilizer Bar (Anti-roll bar): Reduces body roll during cornering.
Helicoidal Spring: Absorbs shocks from the road.
Dampening Set (Shock Absorber): Controls spring movement, reducing bounce.
Note: In FWD cars, the suspension must also accommodate steering and power delivery to the front wheels, making it more compact and complex.
🔧 Rear-Wheel Drive Suspension
Control Arm: Provides wheel alignment and support.
Stabilizer Bar: Prevents excessive body roll.
Helicoidal Spring: Supports vehicle weight and absorbs shocks.
Dampening Set: Same function as in FWD.
Driveshaft: Transfers power from the engine (at the front) to the rear wheels.
Note: RWD setups generally allow for better weight distribution and are simpler at the front since the wheels only steer, not drive.
🚗 Key Difference
FWD: More compact, front handles both steering and power.
RWD: Power sent to the rear, front handles only steering — often gives better balance and handling in performance vehicles.
#mechanic #automotive #machinelearning #mechaniclife #automobile
0 Commentarios
0 Acciones
17 Views