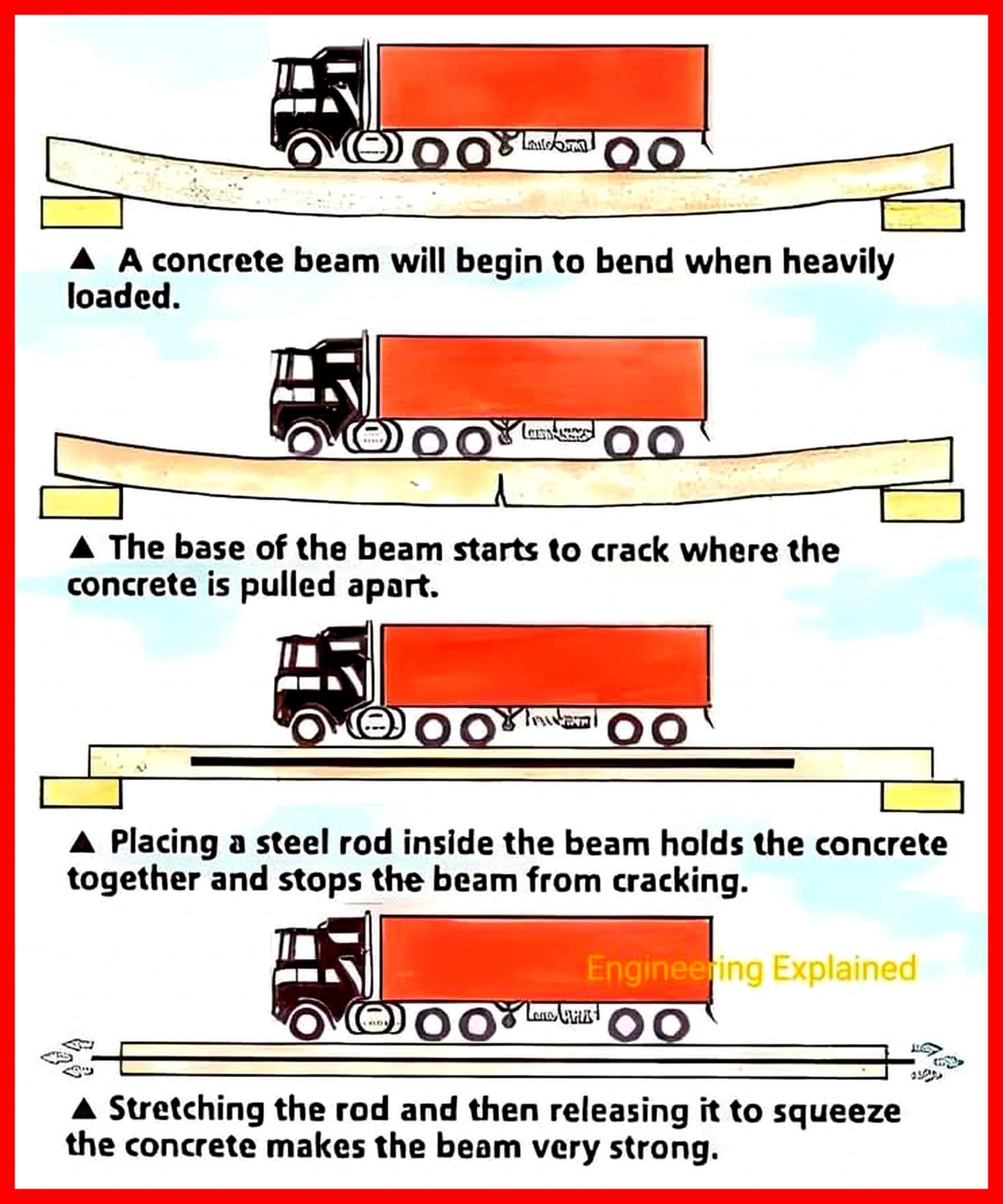
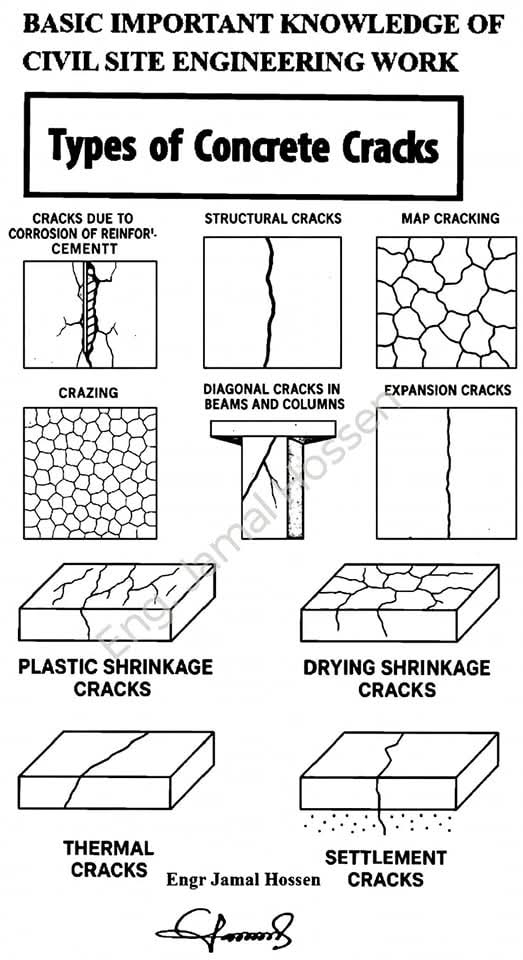
Automobile tires have undergone a remarkable transformation over the last century, evolving from simple rubber coverings into highly engineered components critical for safety, comfort, performance, and efficiency. This evolution reflects changes in vehicle design, road conditions, driving speeds, and advances in material science.
In the early 1900s and 1920s, tires were narrow, tall, and often mounted on spoked wheels. These early tyres were made from natural rubber with cotton fabric plies and had smooth or lightly grooved surfaces. They were designed mainly to cope with rough, unpaved roads and low vehicle speeds. Durability was limited, punctures were common, and ride comfort was basic. Bias-ply construction dominated this era, where fabric layers were laid diagonally across each other, making tires stiff and prone to heat buildup.
By the 1930s and 1940s, tire designs became slightly wider and stronger. Rubber compounds improved, and tread patterns became more defined to enhance grip on wet and muddy roads. During this period, vehicles grew heavier and faster, especially due to wartime engineering advances, pushing tire manufacturers to focus more on load capacity and reliability.
The 1950s marked a major visual and technical shift with the introduction of whitewall tyres, symbolizing style and luxury. More importantly, tire construction continued to improve, offering better comfort and longer life. In the late 1940s and 1950s, radial tire technology was developed, though it gained widespread adoption slightly later. Radial tires used steel belts laid perpendicular to the direction of travel, significantly improving grip, fuel efficiency, and tread life.
During the 1960s and 1970s, radial tires became mainstream globally. Tires grew wider, and tread designs became more aggressive to support higher speeds and better cornering. Performance-oriented tires emerged alongside off-road and all-terrain tires, reflecting the rise of sports cars and utility vehicles. Safety, heat resistance, and handling became central design goals.
By the 1980s and 1990s, tire technology advanced rapidly. Low-profile tyres paired with alloy wheels became popular, improving handling and aesthetics. Rubber compounds were enhanced using synthetic materials, silica, and carbon black to balance grip, durability, and rolling resistance. Specialized tires such as winter tires, high-performance summer tires, and touring tires became common, each designed for specific driving conditions.
From the 2000s onward, tires evolved into highly specialized, technology-driven products. Modern tires feature advanced tread patterns for noise reduction, water dispersion, and improved braking. Run-flat tires allow limited driving even after punctures, while tubeless designs became standard for safety and convenience. Sensors for tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) were integrated to enhance safety.
Today, tires are engineered with sustainability and efficiency in mind. There are eco-friendly tires designed to reduce rolling resistance and improve electric vehicle range, ultra-high-performance tires for sports cars, all-season tires for everyday use, off-road and mud-terrain tires for extreme conditions, and smart tires being developed with embedded sensors to monitor wear, temperature, and road conditions in real time.
From simple rubber rings to intelligent, high-performance components, tire evolution mirrors the progress of the automobile itself focused on safety, efficiency, comfort, and innovation.
#TireEvolution #AutomobileHistory #CarTechnology #RadialTires #VehicleSafety #AutomotiveEngineering #ModernTires #MobilityInnovation #Cars #Tire
In the early 1900s and 1920s, tires were narrow, tall, and often mounted on spoked wheels. These early tyres were made from natural rubber with cotton fabric plies and had smooth or lightly grooved surfaces. They were designed mainly to cope with rough, unpaved roads and low vehicle speeds. Durability was limited, punctures were common, and ride comfort was basic. Bias-ply construction dominated this era, where fabric layers were laid diagonally across each other, making tires stiff and prone to heat buildup.
By the 1930s and 1940s, tire designs became slightly wider and stronger. Rubber compounds improved, and tread patterns became more defined to enhance grip on wet and muddy roads. During this period, vehicles grew heavier and faster, especially due to wartime engineering advances, pushing tire manufacturers to focus more on load capacity and reliability.
The 1950s marked a major visual and technical shift with the introduction of whitewall tyres, symbolizing style and luxury. More importantly, tire construction continued to improve, offering better comfort and longer life. In the late 1940s and 1950s, radial tire technology was developed, though it gained widespread adoption slightly later. Radial tires used steel belts laid perpendicular to the direction of travel, significantly improving grip, fuel efficiency, and tread life.
During the 1960s and 1970s, radial tires became mainstream globally. Tires grew wider, and tread designs became more aggressive to support higher speeds and better cornering. Performance-oriented tires emerged alongside off-road and all-terrain tires, reflecting the rise of sports cars and utility vehicles. Safety, heat resistance, and handling became central design goals.
By the 1980s and 1990s, tire technology advanced rapidly. Low-profile tyres paired with alloy wheels became popular, improving handling and aesthetics. Rubber compounds were enhanced using synthetic materials, silica, and carbon black to balance grip, durability, and rolling resistance. Specialized tires such as winter tires, high-performance summer tires, and touring tires became common, each designed for specific driving conditions.
From the 2000s onward, tires evolved into highly specialized, technology-driven products. Modern tires feature advanced tread patterns for noise reduction, water dispersion, and improved braking. Run-flat tires allow limited driving even after punctures, while tubeless designs became standard for safety and convenience. Sensors for tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) were integrated to enhance safety.
Today, tires are engineered with sustainability and efficiency in mind. There are eco-friendly tires designed to reduce rolling resistance and improve electric vehicle range, ultra-high-performance tires for sports cars, all-season tires for everyday use, off-road and mud-terrain tires for extreme conditions, and smart tires being developed with embedded sensors to monitor wear, temperature, and road conditions in real time.
From simple rubber rings to intelligent, high-performance components, tire evolution mirrors the progress of the automobile itself focused on safety, efficiency, comfort, and innovation.
#TireEvolution #AutomobileHistory #CarTechnology #RadialTires #VehicleSafety #AutomotiveEngineering #ModernTires #MobilityInnovation #Cars #Tire
Automobile tires have undergone a remarkable transformation over the last century, evolving from simple rubber coverings into highly engineered components critical for safety, comfort, performance, and efficiency. This evolution reflects changes in vehicle design, road conditions, driving speeds, and advances in material science.
In the early 1900s and 1920s, tires were narrow, tall, and often mounted on spoked wheels. These early tyres were made from natural rubber with cotton fabric plies and had smooth or lightly grooved surfaces. They were designed mainly to cope with rough, unpaved roads and low vehicle speeds. Durability was limited, punctures were common, and ride comfort was basic. Bias-ply construction dominated this era, where fabric layers were laid diagonally across each other, making tires stiff and prone to heat buildup.
By the 1930s and 1940s, tire designs became slightly wider and stronger. Rubber compounds improved, and tread patterns became more defined to enhance grip on wet and muddy roads. During this period, vehicles grew heavier and faster, especially due to wartime engineering advances, pushing tire manufacturers to focus more on load capacity and reliability.
The 1950s marked a major visual and technical shift with the introduction of whitewall tyres, symbolizing style and luxury. More importantly, tire construction continued to improve, offering better comfort and longer life. In the late 1940s and 1950s, radial tire technology was developed, though it gained widespread adoption slightly later. Radial tires used steel belts laid perpendicular to the direction of travel, significantly improving grip, fuel efficiency, and tread life.
During the 1960s and 1970s, radial tires became mainstream globally. Tires grew wider, and tread designs became more aggressive to support higher speeds and better cornering. Performance-oriented tires emerged alongside off-road and all-terrain tires, reflecting the rise of sports cars and utility vehicles. Safety, heat resistance, and handling became central design goals.
By the 1980s and 1990s, tire technology advanced rapidly. Low-profile tyres paired with alloy wheels became popular, improving handling and aesthetics. Rubber compounds were enhanced using synthetic materials, silica, and carbon black to balance grip, durability, and rolling resistance. Specialized tires such as winter tires, high-performance summer tires, and touring tires became common, each designed for specific driving conditions.
From the 2000s onward, tires evolved into highly specialized, technology-driven products. Modern tires feature advanced tread patterns for noise reduction, water dispersion, and improved braking. Run-flat tires allow limited driving even after punctures, while tubeless designs became standard for safety and convenience. Sensors for tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) were integrated to enhance safety.
Today, tires are engineered with sustainability and efficiency in mind. There are eco-friendly tires designed to reduce rolling resistance and improve electric vehicle range, ultra-high-performance tires for sports cars, all-season tires for everyday use, off-road and mud-terrain tires for extreme conditions, and smart tires being developed with embedded sensors to monitor wear, temperature, and road conditions in real time.
From simple rubber rings to intelligent, high-performance components, tire evolution mirrors the progress of the automobile itself focused on safety, efficiency, comfort, and innovation.
#TireEvolution #AutomobileHistory #CarTechnology #RadialTires #VehicleSafety #AutomotiveEngineering #ModernTires #MobilityInnovation #Cars #Tire
0 Comentários
0 Compartilhamentos
801 Visualizações